Problem
For $∠ABC$ and $∠DEF$, if the sides $AB$ and $DE$ are parallel in the same direction, and $BC$ and $EF$ are parallel in opposite direction, then
$$∠ABC+∠DEF=2∠R.$$
$$ $$
$$ $$
$\downarrow$ $\downarrow$ $\downarrow$ $\downarrow$ $\downarrow$
$$ $$
$$ $$
$$ $$
$$ $$
$$ $$
$$ $$
$$ $$
$$ $$
$$ $$
$$ $$
Solution
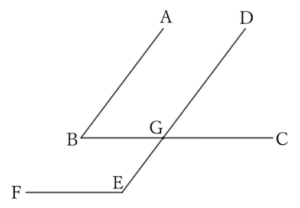
If the intersection of $DE$ and $BC$ is $G$, then $∠ABC$ and $∠BGE$ are alternate angles and $AB∥DE$.
$$∴ \ ∠ABC=∠BGE.$$
$∠BGE$ and $∠DEF$ are interior angles on the same side, and $BC∥EF$.
Therefore, the two angles form complementary angles,
$$∠BGE+∠DEF=2∠R.$$
$$∴ \ ∠ABC+∠DEF=2∠R.$$
$ $
$ $
$ $
Reference
Teiichiro Sasabe (1976) The Encyclopedia of Geometry (2nd edition), Seikyo-Shinsha, p.8