Problem
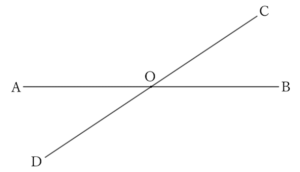
The opposite angles are equal. That is, when two straight lines $AB$ and $CD$ intersect at point $O$,
$∠AOC = ∠BOD$ and $∠AOD = ∠BOC$
$$ $$
$$ $$
$\downarrow$ $\downarrow$ $\downarrow$ $\downarrow$ $\downarrow$
$$ $$
$$ $$
$$ $$
$$ $$
$$ $$
$$ $$
$$ $$
$$ $$
$$ $$
$$ $$
Solution
Since $COD$ is a straight line,
$$∠AOC+∠AOD = 2∠R.$$
Since $AOB$ is also a straight line,
$$∠AOD+∠BOD = 2∠R,$$
$$∴ \ AOC+∠AOD = ∠AOD+∠BOD.$$
$$∴ \ ∠AOC = ∠BOD.$$
Similarly,
$$∠AOD = ∠BOC.$$
$ $
$ $
$ $
Reference
Teiichiro Sasabe (1976) The Encyclopedia of Geometry (2nd edition), Seikyo-Shinsha, p.5