Problem
In $△ABC$, when $∠B=2∠C$,
$$AC<2AB.$$
$$ $$
$$ $$
$\downarrow$ $\downarrow$ $\downarrow$ $\downarrow$ $\downarrow$
$$ $$
$$ $$
$$ $$
$$ $$
$$ $$
$$ $$
$$ $$
$$ $$
$$ $$
$$ $$
Solution
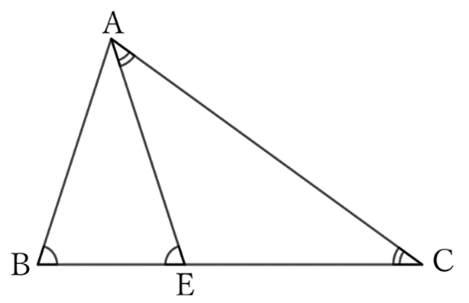
If we take $E$ on $BC$ so that $∠CAE=∠C$,
$$EA=CE.$$
Since $∠AEB$ is the exterior angle of $△EAC$,
$$∠AEB=∠CAE+∠C,$$
$$∴ \ ∠AEB=2∠C,$$
$$∴ \ ∠AEB=∠B,$$
$$∴ \ AB=EA \ (=CE).$$
Regarding $△EAC$, from problem $0042$,
$$AC<EA+CE,$$
$$∴ \ AC<2AB.$$
$ $
$ $
$ $
Reference
Teiichiro Sasabe (1976) The Encyclopedia of Geometry (2nd edition), Seikyo-Shinsha, p.14