Problem
Let $O$ be the intersection of the bisectors of $∠B$ and $∠C$ of a triangle $ABC$, and let $D$ be the intersection of the extension of $AO$ and $BC$. If the perpendicular from $O$ to $BC$ is $OE$, then
$$∠BOE=∠COD.$$
$$ $$
$$ $$
$\downarrow$ $\downarrow$ $\downarrow$ $\downarrow$ $\downarrow$
$$ $$
$$ $$
$$ $$
$$ $$
$$ $$
$$ $$
$$ $$
$$ $$
$$ $$
$$ $$
Solution
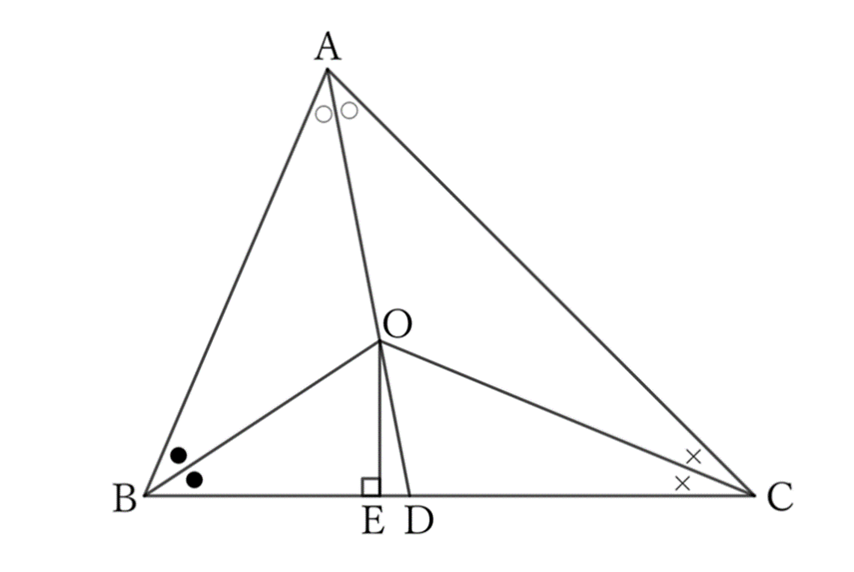
Firstly,
$$∠COD=∠CAO+∠ACO,$$
$$∴ \ ∠COD=\frac{1}{2}∠A+\frac{1}{2}∠C. \qquad [1]$$
Next,
$$∠BOE=∠R-∠OBE,$$
$$∴ \ ∠BOE=∠R-\frac{1}{2}∠B. \qquad [2]$$
However,
$$∠B=2∠R-∠A-∠C,$$
$$∴ \ \frac{1}{2}∠B=∠R-\frac{1}{2}∠A-\frac{1}{2}∠C. \qquad [3]$$
From $[2]$ and $[3]$,
$$∠BOE=∠R-(∠R-\frac{1}{2}∠A-\frac{1}{2}∠C),$$
$$∴ \ ∠BOE=\frac{1}{2}∠A+\frac{1}{2}∠C. \qquad [4]$$
From $[1]$ and $[4]$,
$$∠BOE=∠COD.$$
$ $
$ $
$ $
Reference
Teiichiro Sasabe (1976) The Encyclopedia of Geometry (2nd edition), Seikyo-Shinsha, p.18