From the midpoints $P$ and $Q$ of sides $AB$ and $AC$ of triangle $ABC$, draw perpendicular lines $PD$ and $QE$ to the outside of the triangle such that
$$PD=\frac{1}{2} AB \qquad and \qquad QE=\frac{1}{2} AC.$$
Then, $DM$ and $EM$, which connect $D$ and $E$ to the midpoint $M$ of side $BC$, are equal and perpendicular.
$\downarrow$ $\downarrow$ $\downarrow$ $\downarrow$ $\downarrow$
$$ $$Solution
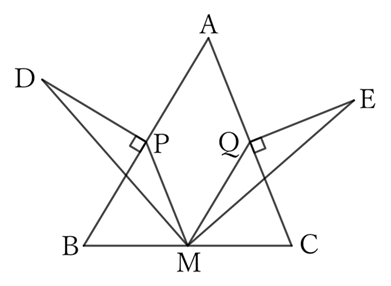
$△ABC$ and $△PBM$ share $∠ABC \ (=∠PBM)$,
$$AB∶PB=2∶1 \qquad and \qquad BC∶BM=2∶1,$$
$$∴ \ △ABC∼△PBM,$$
$$∴ \ ∠BAC=∠BPM,$$
$$∴ \ AQ∥PM.$$
$△ABC$ and $△QMC$ share $∠ACB \ (=∠QCM)$,
$$AC∶QC=2∶1 \qquad and \qquad BC∶MC=2∶1,$$
$$∴ \ △ABC∼△QMC,$$
$$∴ \ ∠BAC=∠MQC,$$
$$∴ \ AP∥QM.$$
Therefore, since quadrilateral $APMQ$ is a parallelogram,
$$PM=AQ,$$
$$∴ \ PM=QE. \qquad (∵ AQ=QE)$$
$$AP=QM,$$
$$∴ \ PD=QM. \qquad (∵ AP=PD)$$
$$△PBM≡△QMC,$$
$$∴ \ ∠BPM=∠MQC,$$
$$∴ \ ∠DPM=∠MQE,$$
$$∴ \ △PDM≡△QME,$$
$$∴ \ DM=ME.$$
Furthermore,
$$∠DME=∠DMP+∠PMQ+∠QME,$$
$$∠PMQ=∠BPM \qquad and \qquad ∠QME=∠PDM,$$
$$∴ \ ∠DME=∠DMP+∠BPM+∠PDM$$
$$=∠DMP+(∠DPM-∠DPB)+∠PDM$$
$$=∠DMP+∠DPM+∠PDM-∠DPB$$
$$=180°-90°=90°.$$
Therefore, $DM$ and $ME$ are orthogonal.
$ $
Reference Teiichiro Sasabe (1976) The Encyclopedia of Geometry (2nd edition), Seikyo-Shinsha, p.39.